Introduction of Human Resource and Economic Development
Human Resource and Economic Development- In the bustling realm of economic progress, the linchpin is none other than Human Resource Development (HRD). This dynamic process involves nurturing the skills, knowledge, and abilities of a workforce, turning them into a powerful catalyst for productivity and performance. In this article, we’ll embark on a journey to uncover the intertwined world of Human Resource and Economic Development, and how this vital relationship fuels prosperity.
Table of Contents
The Engine of Economic Growth
Picture a company as a high-performing vehicle, and the workforce as the engine propelling it forward. Human Resource Development serves as the master mechanic, fine-tuning this engine to ensure it operates at peak efficiency. Similarly, on a larger scale, a skilled and adaptable workforce acts as the driving force propelling a nation toward greater levels of prosperity.
Investing in Skills: A Smart Economic Move
In today’s knowledge-driven economy, the value of skills cannot be overstressed. When individuals possess the right set of skills, they become invaluable assets, not only to their employers but to the entire economy. Imagine a nation investing in training its workforce in cutting-edge technologies. This creates a pool of highly skilled professionals, attracting businesses seeking a competitive edge. This, in turn, leads to a surge in job opportunities, higher incomes, and an overall improvement in the standard of living.
Bridging the Skills Gap
In many economies, there exists a gap between the skills demanded by industries and those possessed by the available workforce. This gap can stymie economic growth. However, with a strategic focus on Human Resource Development, this challenge can be transformed into an opportunity. By offering training programs, workshops, and educational incentives, governments and organizations can bridge this gap, aligning the skills of the workforce with the needs of the economy.
Empowering Through Education
Education is the bedrock of Human Resource Development. A well-educated workforce is more adaptable, innovative, and capable of tackling complex challenges. By investing in education, nations empower their citizens to not only excel in their chosen fields but also contribute significantly to economic progress. For instance, countries with high literacy rates and robust educational systems tend to have more vibrant and diversified economies.
Fostering Innovation and Adaptability
In a rapidly evolving global economy, the ability to innovate and adapt is paramount. A workforce that embraces change and is equipped with the necessary skills is the driving force behind economic resilience. Consider the tech industry, which constantly evolves to meet new demands. Companies leading in this sector owe much of their success to a workforce that embraces continuous learning and innovation.
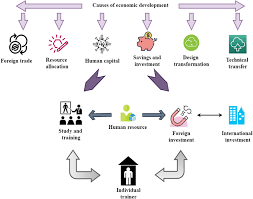
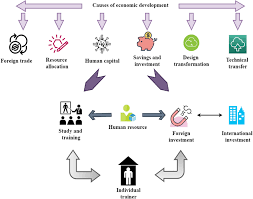
How Human Resource and Economic Development are connected?
Human Resource and Economic Development are intricately connected and have a mutually reinforcing relationship. Here’s how they interact:
- Skilled Workforce Drives Economic Growth: A well-trained and skilled workforce is a critical component of any thriving economy. When individuals possess the necessary skills, they become more productive and contribute significantly to the overall output of a nation. This increased productivity leads to higher levels of economic growth.
- Innovation and Productivity: HRD fosters innovation and productivity within the workforce. Through training, education, and skill-building programs, employees become more adept at finding creative solutions to problems and improving processes. This increased innovation can lead to the development of new products and services, which can, in turn, stimulate economic growth.
- Reduces Unemployment: Effective HRD programs can help reduce unemployment rates by ensuring that individuals have the skills required to fill available job positions. This leads to higher levels of employment and a more efficient allocation of labor resources, which positively impacts economic development.
- Attracting Investments: A skilled workforce is an attractive asset for businesses and industries. Companies are more likely to invest in regions or countries where they can find a capable and well-trained labor force. This can lead to increased foreign direct investment (FDI) and the establishment of new businesses, which contributes to economic development.
- Bridging the Skills Gap: Many economies face a gap between the skills demanded by industries and those possessed by the available workforce. HRD initiatives can address this gap by providing training and education that align with the needs of the job market. This helps to create a workforce that is more closely matched to the demands of the economy.
- Enhances Human Capital: Human capital refers to the collective skills, knowledge, and abilities of a workforce. Investing in HRD enhances a nation’s human capital, which is a critical driver of economic prosperity. A highly skilled workforce is more adaptable, which is particularly important in rapidly changing industries and global markets.
- Raises Income Levels: As individuals acquire new skills and become more productive, their earning potential increases. This, in turn, leads to higher levels of disposable income. When people have more money to spend, it stimulates demand for goods and services, driving economic growth.
- Reduces Income Inequality: HRD initiatives can help reduce income inequality by providing individuals with opportunities for upward mobility. When people have access to education and training, they are more likely to secure higher-paying jobs and improve their socio-economic status.
In summary, Human Resource Development is a linchpin in the process of economic development. It empowers individuals, enriches the workforce, and ultimately propels a nation toward higher levels of prosperity and sustainable growth. The interplay between Human Resource and Economic Development highlights the importance of investing in people as a strategic approach to fostering long-term economic success.
Why Human Resource is Important?
Human Resource (HR) is critically important for several reasons, as it plays a central role in managing an organization’s most valuable asset: its people. Here are some key reasons why Human Resource is important:
- Talent Acquisition and Recruitment:
- HR is responsible for attracting and hiring the right individuals with the skills, qualifications, and cultural fit required for the organization. This ensures that the workforce is equipped to meet the company’s goals and objectives.
- Training and Development:
- HR facilitates the training and development programs necessary to enhance the skills and capabilities of employees. This ensures that they remain competent in their roles and can adapt to evolving job requirements.
- Employee Engagement and Satisfaction:
- HR oversees initiatives aimed at keeping employees engaged, motivated, and satisfied in their work. This includes activities such as performance evaluations, feedback sessions, and creating a positive work environment.
- Performance Management:
- HR establishes performance appraisal systems that help identify areas for improvement, recognize outstanding contributions, and set goals for individual and team performance.
- Conflict Resolution and Employee Relations:
- HR acts as a mediator in disputes or conflicts among employees or between employees and management. They work to create a harmonious work environment that fosters collaboration and teamwork.
- Compliance and Legal Support:
- HR ensures that the organization complies with labor laws, regulations, and industry standards. They provide guidance on legal matters, including employment contracts, workplace safety, and anti-discrimination policies.
- Benefits Administration:
- HR manages employee benefits such as health insurance, retirement plans, and other perks. This includes enrollment, tracking, and addressing any concerns or inquiries related to benefits.
- Strategic Planning and Organizational Development:
- HR plays a pivotal role in aligning human capital with the organization’s strategic goals. They develop and implement policies and practices that support the long-term success of the company.
- Succession Planning:
- HR helps identify and nurture talent within the organization to ensure a smooth transition of leadership and key roles in the event of retirements, promotions, or unforeseen departures.
- Crisis Management and Employee Well-being:
- HR is often involved in crisis management, particularly during emergencies or difficult situations. They are responsible for ensuring the safety and well-being of employees.
- Cultural Stewardship:
- HR helps define, cultivate, and maintain the organizational culture. They play a crucial role in establishing and reinforcing the values, norms, and behaviors that guide the actions of employees.
- Cost Management and Efficiency:
- HR helps manage labor costs by optimizing workforce size and composition. They analyze staffing needs, implement cost-effective hiring strategies, and evaluate the return on investment for HR initiatives.
What if Human Resource and Economic Development Fails?
If Human Resource and Economic Development efforts fail, it can lead to a range of negative consequences for individuals, communities, and the broader economy. Here are some potential outcomes:
- High Unemployment and Poverty:
- Failure in human resource and economic development can result in high unemployment rates and increased poverty levels. This can lead to financial instability, reduced access to basic needs, and diminished overall quality of life.
- Stagnant Economic Growth:
- Without effective human resource and economic development initiatives, a region or country may experience slow or stagnant economic growth. This hinders progress, limits opportunities, and stifles innovation.
- Inequality and Social Disparities:
- Inadequate human resource development can exacerbate existing social inequalities. This can manifest in disparities in income, education, healthcare access, and other areas, leading to social tensions and unrest.
- Lack of Access to Quality Education and Healthcare:
- Failing in human resource development can result in inadequate access to quality education and healthcare services. This perpetuates a cycle of limited opportunities and hampers individual and community well-being.
- Brain Drain and Talent Flight:
- When a region or country fails to invest in human resource development, skilled individuals may seek opportunities elsewhere, leading to a “brain drain.” This exacerbates skills shortages and reduces the potential for innovation and growth.
- Reduced Productivity and Competitiveness:
- Insufficient investment in human capital can lead to a less skilled and less productive workforce. This can erode the competitiveness of businesses and industries in the global market.
- Social Unrest and Political Instability:
- Frustration and dissatisfaction stemming from economic stagnation and lack of opportunities can lead to social unrest and political instability. This can have far-reaching consequences for governance and stability.
- Limited Innovation and Technological Advancement:
- Failing to invest in human resource development can impede innovation and technological advancement. This can result in a lack of competitiveness in industries that rely on cutting-edge technology.
- Environmental Degradation:
- Economic development that is not sustainable or lacks proper environmental safeguards can lead to environmental degradation. This, in turn, can negatively impact the overall well-being of communities.
- Health and Well-being Challenges:
- Inadequate access to healthcare and wellness programs can lead to health challenges, reducing overall workforce productivity and adding strain to healthcare systems.
It’s crucial for governments, organizations, and communities to recognize the importance of effective human resource and economic development initiatives. When these efforts are well-implemented, they can lead to inclusive growth, improved well-being, and a sustainable and prosperous future.
What is Human Resource Development?
Human Resource Development (HRD) is like giving your team superpowers. It’s all about helping your employees grow, learn, and become even better at what they do. Think of it as a boost for your workforce, making them more skilled, confident, and ready to take on new challenges.
Training and Learning: One big part of HRD is training. Imagine sending your team to a workshop or having them learn a new skill online. This helps them do their jobs better and become experts in their fields.
Supporting Growth: HRD also means giving your team the tools they need to succeed. It could be mentorship programs, coaching sessions, or even access to educational resources. This support helps them reach their full potential.
Making Work Fun: Believe it or not, HRD can make work more enjoyable! When employees feel supported and confident, they’re happier. And happy employees are more productive and engaged in their work.
Boosting Confidence: Imagine a team member who used to be nervous about presentations, but with HRD, they become a confident speaker. It’s about helping people believe in themselves and their abilities.
Adapting to Change: In today’s fast-paced world, things are always changing. HRD helps your team roll with the punches. It equips them with the skills to handle new technologies and ways of doing things.
Growing Together: Ultimately, HRD is about growing together. It’s a win-win. Your employees become even better at what they do, and your business thrives because of it.
Conclusion: So, Human Resource Development is like giving your team a power-up. It’s about training, supporting, and boosting confidence. When you invest in your team’s growth, everyone comes out on top. Remember, a strong team is the backbone of a successful business! 💪
What is Resources and Economic Development?
“Resources” refer to the assets, materials, or capabilities that can be used to produce goods and services. These can be natural resources (like minerals, forests, and water), human resources (such as labor, skills, and knowledge), or capital resources (like machinery, infrastructure, and technology).
“Economic development” refers to the sustained improvement in the economic well-being and standard of living of a community, region, or country. It involves various factors, including increasing income levels, reducing poverty, improving infrastructure, and creating opportunities for employment and entrepreneurship.
The relationship between resources and economic development is crucial. Resources are the building blocks that enable economic activities to take place. They can be harnessed and utilized to drive economic growth, which, in turn, leads to higher living standards and an improved quality of life for a population.
For example, a country with abundant natural resources like oil or minerals can use these resources to generate revenue, invest in infrastructure, and create jobs, contributing to economic development. Similarly, a well-educated and skilled workforce (a human resource) can lead to higher productivity, innovation, and competitiveness, which are key drivers of economic development.
In summary, resources provide the means for economic development, and effective management and utilization of these resources are essential for sustainable and inclusive economic growth.
Cases Where Human Resource Development Plays an Important Role?
Human Resource Development (HRD) plays a critical role in various scenarios within organizations. Here are some cases where HRD is particularly important:
- New Employee Onboarding:
- HRD ensures that new hires receive proper orientation, training, and support to integrate smoothly into the organization. This helps them become productive and engaged team members.
- Skills Training and Development:
- HRD identifies skill gaps within the workforce and provides training programs to enhance employees’ capabilities. This could include technical skills, leadership development, and soft skills training.
- Performance Improvement Plans:
- When an employee’s performance falls below expectations, HRD collaborates with managers to create improvement plans. This may involve additional training, coaching, or mentoring to help the employee meet performance goals.
- Succession Planning:
- HRD identifies high-potential employees and prepares them for future leadership roles within the organization. This ensures a smooth transition in case of promotions or retirements.
- Change Management and Organizational Transformation:
- During times of organizational change or restructuring, HRD plays a crucial role in training employees to adapt to new systems, processes, and roles. This helps minimize resistance and supports a smooth transition.
- Diversity and Inclusion Initiatives:
- HRD implements programs to foster diversity and inclusion in the workplace. This may include training on cultural sensitivity, unconscious bias, and inclusive leadership.
- Employee Engagement and Retention:
- HRD develops initiatives to boost employee engagement, job satisfaction, and overall well-being. This can include wellness programs, career development opportunities, and recognition programs.
- Conflict Resolution and Mediation:
- HRD provides support in resolving conflicts between employees or between employees and management. They may offer conflict resolution training or facilitate mediation sessions.
- Compliance and Legal Training:
- HRD ensures that employees are educated about company policies, industry regulations, and legal requirements. This helps mitigate legal risks and maintain a compliant workplace.
- Adapting to Technological Advancements:
- As technology evolves, HRD provides training and development programs to help employees adapt to new tools, software, and systems used in the workplace.
- Customer Service and Client Interaction:
- In industries where client interactions are crucial, HRD may provide training on customer service skills, effective communication, and relationship-building.
- Crisis and Emergency Response Training:
- HRD prepares employees to respond effectively in emergency situations, ensuring their safety and the well-being of others in the organization.
These cases demonstrate the diverse and critical role that Human Resource Development plays in nurturing a skilled, engaged, and adaptable workforce, ultimately contributing to the overall success of the organization.

10 FAQs On Human Resource and Economic Development
Certainly! Here are 10 frequently asked questions (FAQs) about the connection between Human Resource and Economic Development along with their answers:
- Q1: What is the relationship between Human Resources and Economic Development?
- A1: Human Resources and Economic Development are closely intertwined. Human resources, including skilled labor, education, and healthcare, are vital inputs for economic growth and development.
- Q2: How does a skilled workforce contribute to economic development?
- A2: A skilled workforce is essential for driving innovation, productivity, and competitiveness in industries. It attracts investment, enhances productivity, and supports sustainable economic growth.
- Q3: What role does education play in economic development?
- A3: Education is a fundamental component of human capital development. It equips individuals with the knowledge and skills needed for employment, entrepreneurship, and contributing to the economy.
- Q4: How does healthcare impact economic development?
- A4: A healthy population is more productive and better able to participate in the labor market. Good healthcare improves workforce productivity, reduces absenteeism, and lowers healthcare costs for employers.
- Q5: Can investing in workforce training and development lead to economic growth?
- A5: Yes, investing in workforce training and development enhances the skills and capabilities of employees, which in turn leads to higher productivity, innovation, and overall economic growth.
- Q6: What are the key challenges in aligning Human Resources with Economic Development?
- A6: Challenges may include ensuring equal access to education and healthcare, addressing skills gaps, promoting inclusive growth, and adapting to technological advancements in the workforce.
- Q7: How can governments promote Human Resource development for economic growth?
- A7: Governments can implement policies that prioritize education, healthcare, skills training, and workforce development. They can also create an enabling environment for businesses and innovation.
- Q8: How does Human Resource development impact income inequality?
- A8: Effective Human Resource development can help reduce income inequality by providing individuals with opportunities for skill development, education, and access to better jobs and income-generating activities.
- Q9: Are there examples of countries that have successfully leveraged Human Resource for economic development?
- A9: Countries like South Korea, Singapore, and Finland have effectively invested in education, skills training, and healthcare to develop highly skilled workforces, which has contributed significantly to their economic success.
- Q10: Can economic development strategies lead to improved Human Resource outcomes?
- A10: Yes, economic development strategies that focus on creating jobs, fostering entrepreneurship, and investing in education and healthcare can lead to improved Human Resource outcomes and overall well-being.
These FAQs provide a foundational understanding of the critical relationship between Human Resource and Economic Development. They highlight the importance of investing in human capital for sustainable economic growth and prosperity.

References
- https://www.eesc.europa.eu/sites/default/files/resources/docs/king-fr.pdf
- https://edurev.in/question/1379336/Describe-in-brief-the-role-of-humanresources-in-economic-development-

